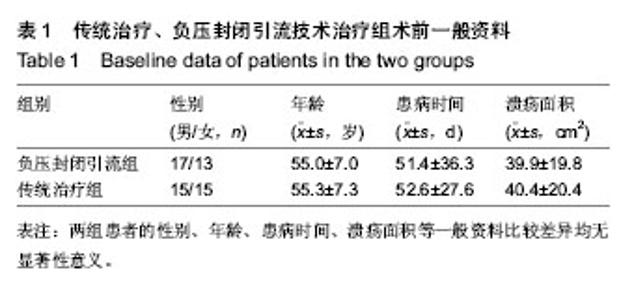
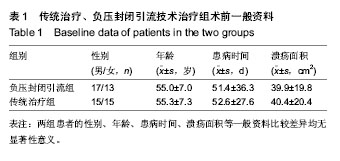
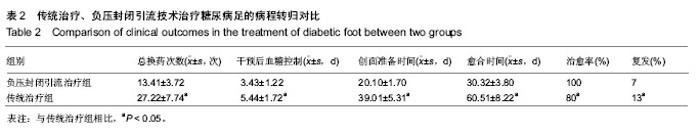
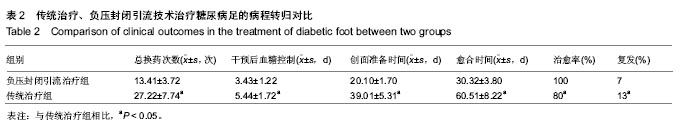
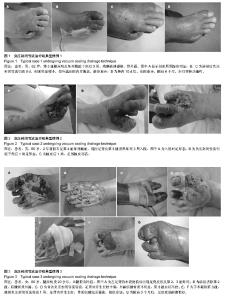
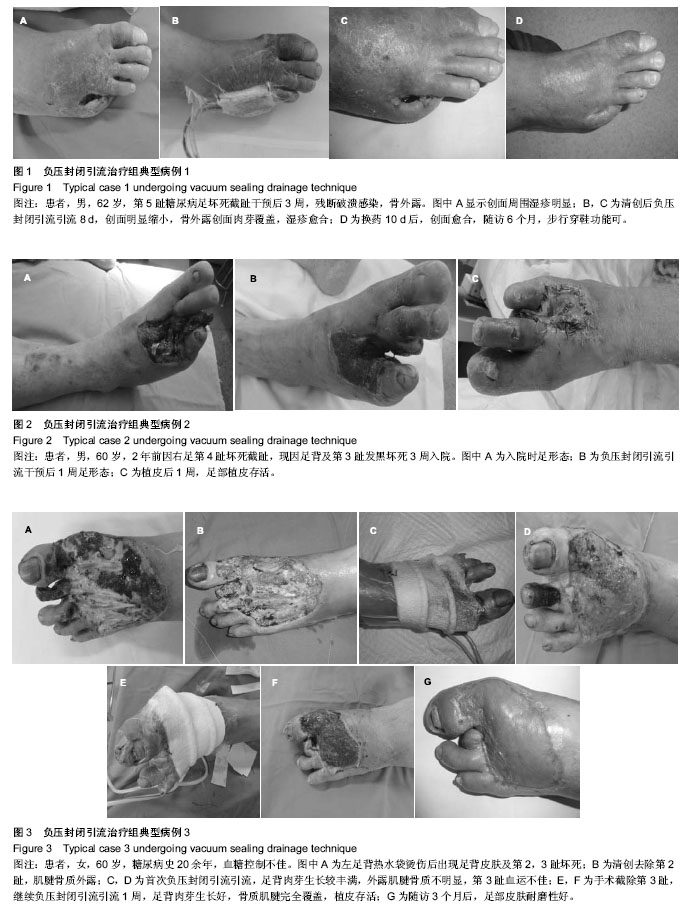
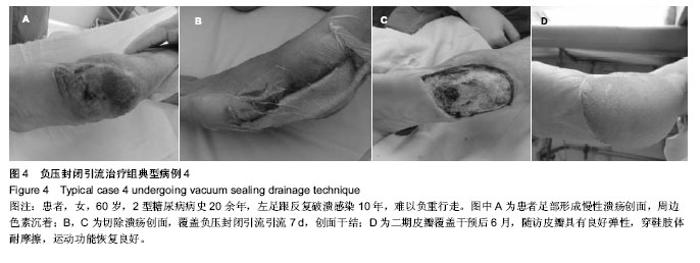
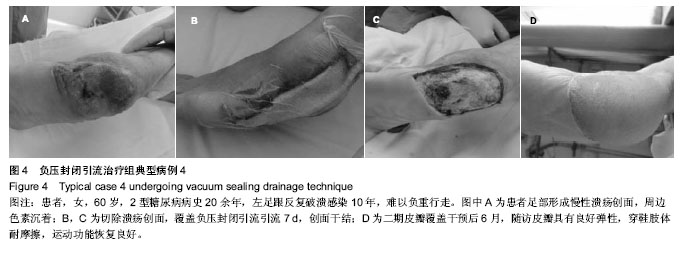
| [1] 朱敬,刘之川.负压封闭引流技术治疗糖尿病足疗效观察[J].现代医药卫生,2013,29(13):1946-1947.
[2] 徐俊.王鹏华.表皮生长因子治疗糖尿病足溃疡的研究进展[J].国际内分泌代谢杂志,2007,27:S44-S46.
[3] 姜春艳,刘艳.糖尿病足危险因素分析[J].临床荟萃,2010,25(4): 336-338.
[4] 毋强华.VSD负压吸引治疗糖尿病足感染的疗效分析[J].医学理论与实践,2012,25(12):1472-1473.
[5] Robson M, Steed D, Franz M. Wound healing: biologic features and approaches to maximize healing trajectories. Current Prob Surg. 2001;38:61-140.
[6] 戚晓冬,付士平,孙平.负压吸引技术修复骨科创面的疗效分析[J].当代医学,2014,20(3):69-70.
[7] State Council of the People's Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01.
[8] 黄崇友,臧晓方,熊军,等.负压封闭引流技术治疗糖尿病足难愈创面32例[J].中国医学创新,2012,9(222):32-33.
[9] 马永刚,廖琦,张春.负压封闭引流治疗糖尿病足溃疡12例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012,20(4):35-36.
[10] 肖金丽,徐斌,夏云,等.负压吸引系统在糖尿病足伴感染中的应用[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2013,35(1):97-99.
[11] 代庆春,张敏,姚元章.真空封闭引流在创伤修复中应用的现状和展望[J].创伤外科杂志,2007,4(9):371-373.
[12] 刘朋飞.负压吸引在创面修复中的研究进展[J].西部医学, 2013, 25(8):1274-1276.
[13] 韩焱福,徐光,周京志,等.负压创面治疗结合植皮术修复糖尿病足溃疡的临床研究[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(10):88-90.
[14] Frykberg RG. Diabetic foot ulcerations.In:Frykberg RG,ed. The high risk foot in diabetes mellitus. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone, USA. 1991:151.
[15] Ziegler MD, Sohr CG, Nourooz-Zndeh J. Oxidat ive stress and antiox idan t defen se in relat ion to the severity of diabetic polyneuropathy and card iovascular autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2178-2183.
[16] Fleischmann W, St recker W, Bombelli M, et al. Vacuum sealing astreatment of soft tissue damage in open fractures. Unfallchirurg. 1993;96(3):488-492.
[17] 裘华德.负压封闭引流技术[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2003.
[18] 曹大勇,陈绍宗,汤苏阳,等.封闭式负压引流技术对人慢性创面血管生成的影响[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(2):264-265.
[19] 周建大,刘进言,胡媛,等.负压引流与创面修复[J].中国全科医学, 2009,12(58):913-915.
[20] 杨润功,张伟佳,侯树勋,等.负压封闭引流在Gustilo ⅢB和ⅢC型开放性骨折感染治疗中的应用[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病, 2008,(4): 193-197.
[21] 罗江蓉,岑瑛.负压封闭引流装置促进创面愈合的机制[J].四川医学,2013, 34(10):1599-1601.
[22] 华小霞.负压封闭引流技术(VSD)对各种复杂[J].医学美学美容, 2013(6):80-81.
[23] Y'mocy J, Aibles JM, Wickc C, et al. Treatment of periprosthetic soft tissue infection of the groin following vascular surgical procedures by means of a polyvinyl alcohol-vacuum sponge system. Wound Repair Regen. 2003; 11(2):104-109.
[24] 王春喜,卢怡,王晓勇.负压封闭引流促进创伤修复机制的研究进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2009,11(2):184-186.
[25] 王明程,王宇,毛凤菊.负压封闭引流技术在创伤修复机制中的研究进展[J].中国医药科学, 2011,1(7):62-63.
[26] Driver VR, Madsen J, Goodman RA. Reducing amputation tates in patients with diabetes at a military medical center the limb preservation service model. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(2): 248-253.
[27] Akbari CM, Pomposelli FB Jr. Diabetes and diseases of the foot. IM Int Med. 2000;21:10-17.
[28] 玛丽亚.糖尿病足感染的抗生素治疗[J].糖尿病天地, 2011,5(11): 526-528.
[29] 史国珍,王先桥,何效梅,等.前列地尔脂微球载体制剂治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变近期疗效[J].中国临床康复,2002,6(17):2619.
[30] 唐兰,朱西娥,梁乙安,等.川芎嗪对糖尿病周围血管病变的疗效初探[J].中国糖尿病杂志,1997,5(6):323-326.
[31] 关小宏,李宝军,杨彩哲,等.糖尿病足主要感染细菌及抗感染治疗[J].河北医药,2013,35(2):260-261.
[32] 流沙,陈兵,梁自文,等.亲水性敷料治疗糖尿病足性溃疡40例疗效观察[J].重庆医学,2006,35(5):462.
[33] 胡骁骅,张普柱,孙永华,等.纳米银抗菌医用敷料银离子吸收和临床应用[J].中华医学杂志,2003,83(24):2178-2179.
[34] 李仕明.糖尿病足与相关并发症的诊治[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2002.
[35] 余林薪,段洪,刘晓天,等.负压封闭引流技术在肢体重度创伤中的运用体会[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2014,11(1):36. |